L-Glutamine:General description,Application,and Production
Apr 26,2023
L-glutamine (L-Gln) is a non-essential amino acid, which means that it can be synthesized by the human body and is not required to be obtained through the diet. It is the most abundant amino acid in the human body, with high concentrations found in the skeletal muscle, lung, liver, brain, and other organs. L-glutamine plays various roles in the body, including serving as a source of energy, a precursor for nucleotide and protein synthesis, and a regulator of acid-base balance. It is also involved in immune function, intestinal health, and the maintenance of muscle mass. Due to its important physiological functions, L-glutamine has been studied for its potential therapeutic applications in conditions such as cancer, inflammatory bowel disease, and trauma. L-glutamine can be obtained through the diet, with sources including meat, fish, dairy, and certain vegetables. It is also available as a dietary supplement in various forms, including capsules, powder, and liquid[1].
Application and Pharmacology
In recent years, with the deepening and development of research on the physiological, biochemical, and clinical aspects of L-glutamine, its importance to life has become increasingly prominent and is considered one of the most important amino acids currently known. In Germany, glutamine is included in the pharmacopoeia as a drug due to its excellent therapeutic effect on diseases such as gastric ulcers, gastritis, and duodenal ulcers; In Japan, L-glutamine has been widely used as a gastrointestinal drug and brain building product; In the United States, health products used to treat diseases such as gastric ulcers and nutritional supplements for athletes have led to the widespread use of L-glutamine. It is precisely because L-glutamine has very physiological functions and its wide applications in food, medicine, nutrition and health, feed, etc. that it greatly stimulates and promotes the rapid development of the glutamine industry. With the progress of healthcare, the accumulation of wealth, and the continuous increase in people's understanding of glutamine, the role and function of glutamine will be fully developed. Pharmaceutical and nutritional supplements based on glutamine will have a broader market, and it will also greatly promote the further development of China's health industry.
The Emerging Role of L-Glutamine in Cardiovascular Health and Disease Emerging evidence indicates that L-Glutamine plays a fundamental role in cardiovascular physiology and pathology . By serving as a substrate for the synthesis of DNA, ATP, proteins, and lipids, Gln drives critical processes in vascular cells, including proliferation, migration, apoptosis, senescence, and extracellular matrix deposition. Furthermore, L-Glutamine exerts potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects in the circulation by inducing the expression of heme oxygenase-1, heat shock proteins, and glutathione. L-Glutamine also promotes cardiovascular health by serving as an l-arginine precursor to optimize nitric oxide synthesis. Importantly, L-Glutamine mitigates numerous risk factors for cardiovascular disease, such as hypertension, hyperlipidemia, glucose intolerance, obesity, and diabetes. Many studies demonstrate that L-Glutamine supplementation protects against cardiometabolic disease, ischemia-reperfusion injury, sickle cell disease, cardiac injury by inimical stimuli, and may be beneficial in patients with heart failure[2].
Synthesis
The production methods of glutamine mainly include chemical synthesis, fermentation, and enzymatic methods[3]:
1.Chemical synthesis:Chemical synthesis is a method of producing or preparing amino acids by combining organic synthesis and chemical engineering. There are six chemical synthesis pathways for L-glutamine, and the following two main synthesis methods are introduced: In the 1940s and 1950s, foreign countries proposed the traditional method of industrial synthesis of L-glutamine by esterification, synthesis, addition, and hydrolysis of L-glutamic acid as raw material under the catalysis of sulfuric acid. This method first esterifies L-glutamic acid with methanol, then adds carbon disulfide to react with the amino group to form amino dithiomethane ammonium to protect the amino group. Ammonia is then introduced until saturation, and the mixture is allowed to stand for 4-5 days. Afterward, the ammonia is removed by vacuum concentration, and ice acetic acid is added to remove the carbon disulfide. The solvent is then evaporated under reduced pressure to obtain L-glutamine. This process has been used in industrial production. This process route utilizes the currently widely available and inexpensive L-glutamic acid as the raw material, with simple operation, mild conditions, and easy control. However, this method has a long process route and a low yield. The resulting esterification liquid needs to be neutralized with ammonia, resulting in a large amount of sulfur ammonia by-product. Currently, this method is mostly used in China. The process route is as follows(Figure 1):
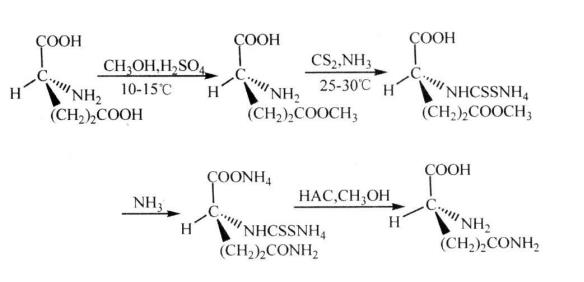
Figure 1 Traditional chemical synthesis process of L-glutamine
2. First, L-glutamic acid methyl ester was synthesized, which was then directly reacted with hydroxylamine hydrate to obtain L-glutamyl hydroxylamine. Finally, reduction with Raney nickel yielded L-glutamyl amide. The synthesis process diagram shows that concentrated sulfuric acid is a necessary reagent in each step, and a large amount of carbon disulfide is required. The conditions are relatively harsh and difficult to control, and the yield is low due to the multiple steps. Although the second method has some improvements, it is still complicated and requires the use of a catalyst, which imposes new requirements on the process conditions and makes the process still complex. The synthesis method uses a large amount of chemical reagents, and there will be residual amounts of these reagents to varying degrees in the final product. As an orally administered drug, L-glutamyl amide has high purity requirements. Using the synthesis method restricts the quality of the product and its range of use. Moreover, the use of the synthesis method will have adverse effects on the environment and increase the cost of the product.
3.Glutamine synthetase (GS) is the key enzyme responsible for L-glutamine synthesis. However,enzymatic activity of GS is influenced by many factors,leading to the low enzyme activity and the low production of L-Gln. In order to improve the yield of L-Gln,a high-effective expression system was constructed in Corynebacterium glutamicum with gln A gene. We tested two different strong promoters,promoter tac ( Ptac) , and promoter mal ( Pmal ) , for a comparison of the activity of GS. After then,for avoiding the adenylylation in C. glutamicum,we constructed plasmids containing the point mutation of glnA,in which Tyr 405 is replaced by a phenylalanine residue.Since the glutamine synthetase in Bacillus subtilis is not regulated via adenylylation,we also compared C. glutamicum GS activity with Bacillus subtilis’s to detect the enzyme activity in the given system. Light point of this study is to express GS of Bacillus subtilis in C. glutamicum expression system for the first time. The results reveal that promoter tac was more capable for producing L-Gln in C. glutamicum system.GS enzyme from Bacillus subtilis had the higher activity than C. glutamicum's. The recombinant strain BJ2 has the highest GS activity and produce 32.5 g /L L-glutamine[4].
Toxicity and safety
L-glutamine is generally considered safe and well-tolerated when consumed in recommended doses. It is an amino acid that is naturally present in the human body and is also obtained through dietary sources. In clinical studies, oral doses of up to 0.65 grams per kilogram of body weight per day for up to 30 days have been found to be safe and well-tolerated in healthy adults. However, in rare cases, some people may experience mild gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, or abdominal pain when consuming high doses of L-glutamine supplements. Individuals with liver or kidney disease, as well as pregnant or breastfeeding women, should consult with their healthcare provider before taking L-glutamine supplements.
There is no evidence to suggest that L-glutamine is toxic at recommended doses. The LD50 (median lethal dose) of L-glutamine in animals is very high, indicating a low potential for acute toxicity. However, excessive doses of L-glutamine may lead to elevated levels of ammonia in the blood, which can be harmful to individuals with liver disease or other metabolic disorders. Overall, L-glutamine is considered safe when consumed in recommended doses, and toxic effects are not expected at these doses. However, as with any supplement or medication, it is important to follow recommended dosages and consult with a healthcare provider before use, especially in individuals with underlying medical conditions.
Reference
1.Han Shufen and E Dongli: "Overview and Economic Benefits of L-Glutamine Production and Research at Home and Abroad", Inner Mongolia Petrochemical Industry, 2010, Issue 22, pp. 36-37.
2.
3.Ding Bangqin, Qiu Xin, and Zhou Feng: "Overview of the Biochemical Properties, Uses, and Production Methods of L-Glutamine", Amino Acids and Biological Resources, Issue 04, 2008, pp. 42-45.
4.Bai Jing, Wu Tongsiyu, Wang Qi, et al.: "Efficient expression of glutamine synthase from Bacillus subtilis using glutamic acid rod-shaped bacteria to produce L-glutamine through fermentation." Journal of Nanjing Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 2015, Issue 02, pp. 78-85.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- L-Glutamine: Versatile Amino Acid with Roles in Intestinal Microbiome Modulation and Anti-Inflammatory Oct 28, 2024
L-Glutamine is a non-essential amino acid present abundantly throughout the body and is involved in many metabolic processes. It is synthesized from glutamic acid and ammonia.
Hexamethyldisilazane, also known as HMDS and bis(trimethylsilyl)amine, is an organosilicon compound.The molecule is a derivative of ammonia with trimethylsilyl groups in place of two hydrogen atoms.....
Apr 26,2023Organic reagents1-(3-Dimethylaminopropyl)-3-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride, also known as EDC·HCl, is a popular carbodiimide coupling reagent used in bioconjugation chemistry.....
Apr 26,2023APIL-Glutamine
56-85-9You may like
- L-Glutamine
-

- $1.00 / 1KG
- 2025-04-18
- CAS:56-85-9
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 10 mt
- L-Glutamine
-

- $6.00 / 1kg
- 2025-04-17
- CAS:56-85-9
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 2000KG/Month
- L-Glutamine
-

- $0.00 / 1Kg/Bag
- 2025-04-16
- CAS:56-85-9
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 98.5%-101.5%; FCC
- Supply Ability: 10 TONS